Throughout history, medieval rulers frequently used torture and imprisonment as tools of political suppression. Those labeled as threats-whether through rebellion, dissent, or simply opposing views-faced severe medieval punishment for political offenses. Understanding how political prisoners were treated in the Middle Ages provides crucial insights into the brutal realities of medieval justice for political criminals.
Medieval Rulers and Political Prisoners
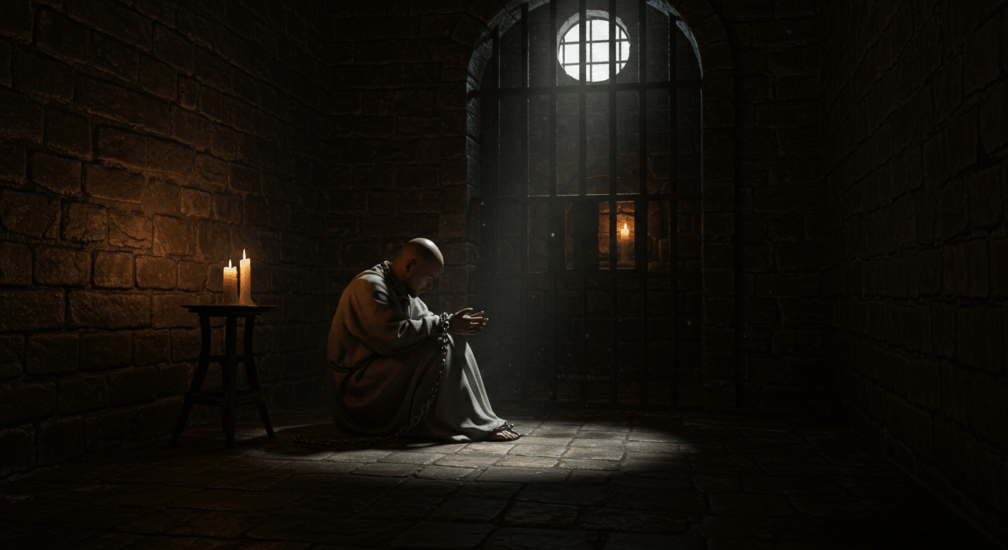
In medieval Europe, rulers had absolute authority, and maintaining power often involved harsh measures against perceived threats. Political prisoners, defined as captives held primarily for their ideological or political beliefs, experienced relentless persecution. Whether nobles plotting rebellion or common citizens challenging royal decrees, individuals faced imprisonment, cruelty, and systematic oppression designed to crush dissent.
Medieval Prisons for Political Prisoners
Medieval prisons for political prisoners were notoriously grim and inhumane. Captivity often meant confinement in dungeons, characterized by darkness, isolation, and unsanitary conditions. Prisoners endured long periods chained to walls, suffering from starvation and disease, exacerbated by psychological torment.
Notorious facilities like the Tower of London or Château d’If exemplified the severe brutality prisoners faced. Dungeons weren’t just for holding captives-they symbolized the total authority of rulers to enforce their will through imprisonment.
Torture as Political Suppression
Torture of political prisoners wasn’t merely punitive-it was deliberately used to extract confessions, obtain information, and instill fear among the populace. Medieval authorities believed torture to be an effective interrogation technique, despite its inherent cruelty and the questionable reliability of the obtained confessions.
Common torture methods included the rack, where victims were stretched to unbearable extremes, or the Iron Maiden, whose spikes inflicted severe pain and often death. Such brutality served as both punishment and a stark warning against potential rebellion.
Political Prisoners and the Inquisition
The Inquisition played a notorious role in targeting political prisoners, especially those accused of heresy or challenging church authority. Often, political motives intertwined with religious accusations, allowing inquisitors to justify their severe measures. Prisoners were subject to prolonged interrogation and torture, leaving lasting scars both physically and mentally.
The notorious auto-da-fé-a public spectacle combining punishment and execution-illustrates the extent of cruelty prisoners faced, emphasizing the intersection of religion, politics, and public persecution.
Creepy Attractions in Chicago: Exploring Medieval Torture
Modern museums, such as the creepy attractions in Chicago at the Medieval Torture Museum, offer vivid recreations of the instruments and conditions political prisoners faced. These exhibits provide powerful, immersive experiences, illustrating the dark side of medieval history.
Visitors can witness historically accurate replicas of medieval torture instruments and dungeons, bringing history vividly to life and deepening our understanding of political persecution.
Discovering More Across the U.S.
For those intrigued by this chilling aspect of history, visits to other locations can further enrich understanding. The Medieval Torture Museum in Los Angeles and the Medieval Torture Museum in Saint Augustine offer equally compelling explorations into medieval punishment methods and the stories behind the political prisoners who endured them.
Deepen Your Understanding Through Our Blog
To further explore medieval punishment methods, prisoner stories, and insights into historical political suppression, follow our regularly updated blog. It provides detailed accounts, historical analyses, and surprising insights into the brutal past.
Remembering History
Examining how political prisoners were treated in the Middle Ages isn’t merely a historical curiosity-it’s a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked power. Recognizing this dark chapter of history encourages reflection on the importance of safeguarding political freedom and human rights, ensuring that such brutality never recurs.
Explore, learn, and remember the importance of empathy and justice in shaping our world.