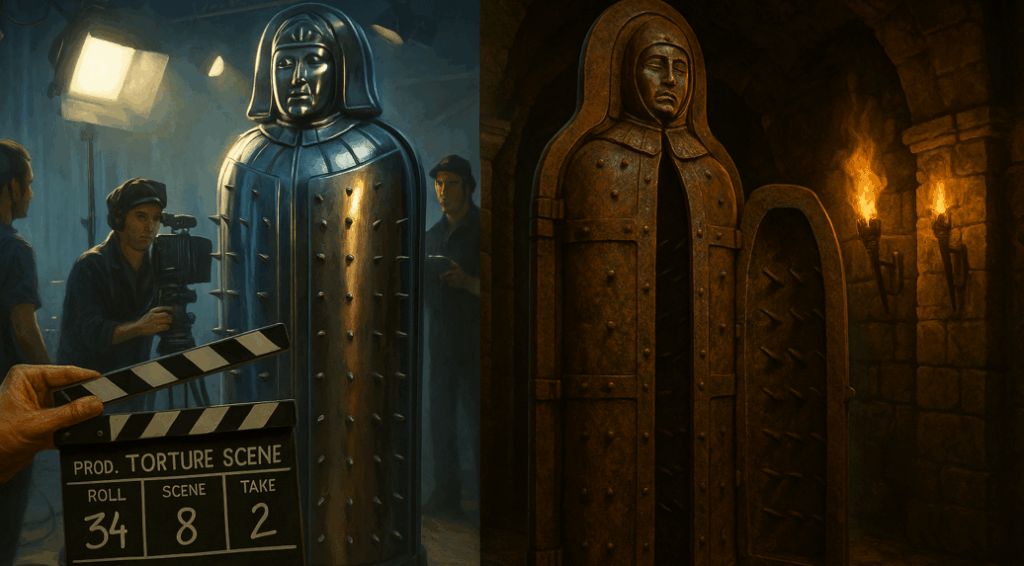The Middle Ages were a time of great warfare and violence, leading to countless injuries and death on the battlefield. While torture was often used to extract confessions or punish enemies, medieval field hospitals provided a different kind of care — one focused on healing the wounded. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating history of medieval medicine, how battlefield medical treatments worked, and the role of medieval battlefield surgeons in the treatment of injuries. Let’s take a deeper look at how medieval hospitals treated wounds and helped soldiers survive the aftermath of brutal battles.
History of Medieval Medicine:
Medieval medicine was based on a mixture of ancient Greek and Roman knowledge, combined with some rudimentary practices developed during the Middle Ages. Physicians during this period were often monks, who had access to medical texts and knowledge from the ancient world, but also relied on their own experience and rudimentary remedies. The development of medieval healthcare during war was greatly influenced by the need to treat injuries sustained in battle, as well as the diseases that often spread among soldiers in the field. The battlefield was a place of great suffering, but it also gave birth to the evolution of medical practices that are still used today.
Battlefield Medical Treatments in the Middle Ages:
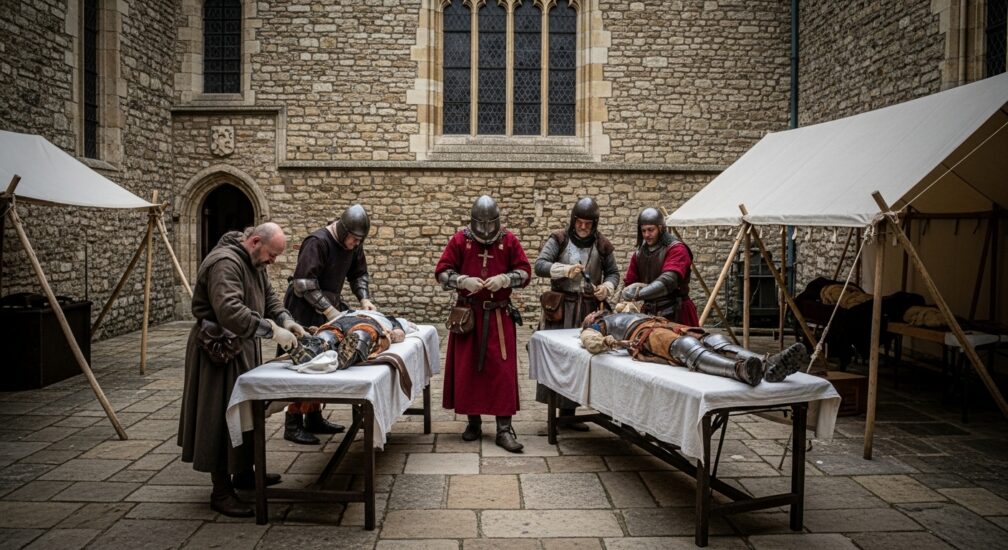
On the battlefield, medieval battlefield surgeons worked tirelessly to treat the wounded, often under difficult conditions. The main treatments for injuries included cauterization, herbal remedies, and rudimentary surgeries. Wounds caused by weapons such as swords, arrows, and spears were common, and many of these injuries were life-threatening. Medieval soldiers often suffered from broken limbs, infected wounds, and amputations. In some cases, battlefield medical treatments could save a soldier’s life, but in other instances, death was the only outcome.
One of the most common treatments for wounds during this time was the use of boiling oil to cauterize the wound and stop bleeding. Surgery was performed with basic tools, often by untrained physicians or battlefield medics, who were familiar with the effects of injury and could provide basic care. Despite the primitive methods, many soldiers did survive and return to the battlefield after receiving treatment.
How Medieval Hospitals Treated Wounds:
In medieval times, field hospitals were set up near the battlefield to treat the wounded. These hospitals, often located in churches or monasteries, became centers of medical care. Medieval hospitals were typically run by monks or nuns, who had some training in medical practices. The treatment in these hospitals focused on cleansing wounds, preventing infections, and providing pain relief. Medieval war injuries were treated with poultices made from herbs and natural remedies to prevent infection and promote healing.
Surgeons in medieval hospitals were skilled in medieval trauma care and often had specialized knowledge in treating battlefield injuries. Their medical practices were heavily influenced by religious beliefs, and many treatments were thought to have spiritual healing properties. Despite the limited technology available, medieval hospitals were often able to help soldiers survive wounds that would otherwise have been fatal.
Medieval Torture Devices and Hauntings:
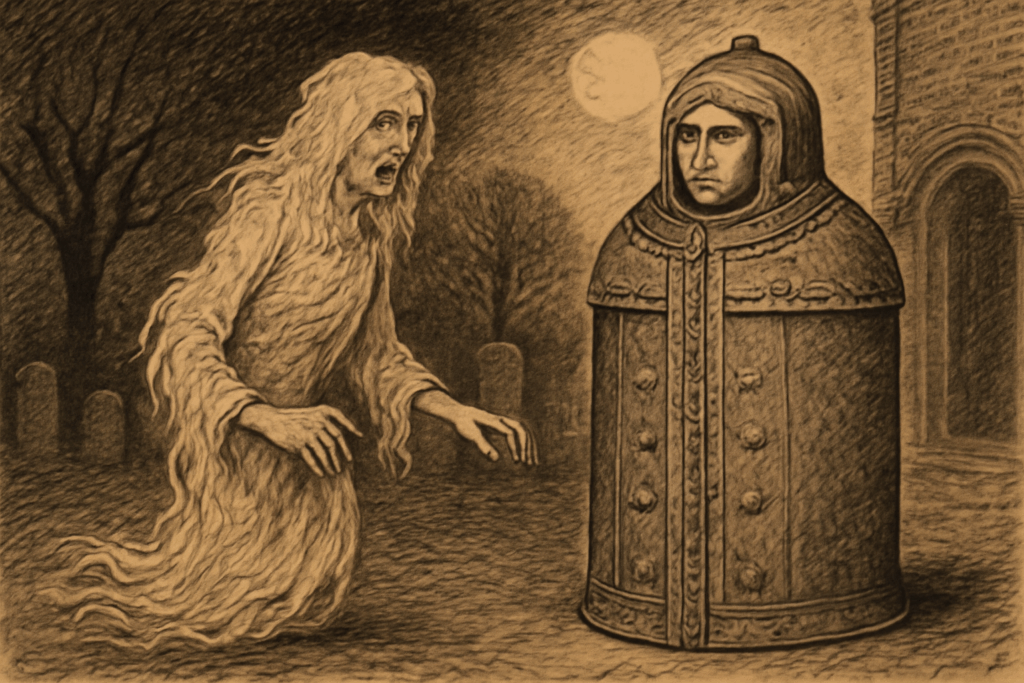
While the primary focus of medieval medical care was to treat injuries sustained in battle, the era was also known for its use of torture devices. Some of the most famous and gruesome medieval torture devices were designed to inflict extreme pain and suffering on prisoners. These devices, including the infamous Iron Maiden, were used to extract confessions from criminals or enemies of the state.
Interestingly, these devices, now displayed in Medieval Torture Museums around the world, also carry with them a haunting history. Many believe that the spirits of those who suffered in these devices haunt the locations where they were once used. Visitors to places like the Medieval Torture Museum in Chicago can explore the chilling history of these devices and experience firsthand the dark past of medieval justice.
The Role of Battlefield Surgeons:
The battlefield surgeons of the medieval era played a vital role in the medical care of soldiers. These men and women were often untrained or had limited education in medical practices, but their experience in treating battlefield injuries made them invaluable during times of war. Their work saved countless lives, and their techniques formed the foundation of modern surgical practices.
The role of a battlefield surgeon was not without risk, as they often had to work under dangerous and unsanitary conditions. However, the medieval battlefield surgeon was essential to the survival of soldiers during these brutal times. Some of the techniques they used, such as the creation of rudimentary bandages and splints, are still in use today, although modern medicine has improved vastly.
The history of medieval medicine and battlefield care is a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of medical practitioners during the Middle Ages. Despite the limitations of technology and knowledge, medieval physicians and surgeons played a critical role in saving the lives of soldiers who would otherwise have perished from their injuries. The legacy of medieval medical practices continues to influence modern medicine, and the incredible work done by these early physicians should never be forgotten.
For more about medieval torture devices and the fascinating history of medieval medical care, visit the Medieval Torture Museum in St. Augustine or read more on our blog. You can also check out the Medieval Torture Museum in LA for more chilling experiences and historical insights.