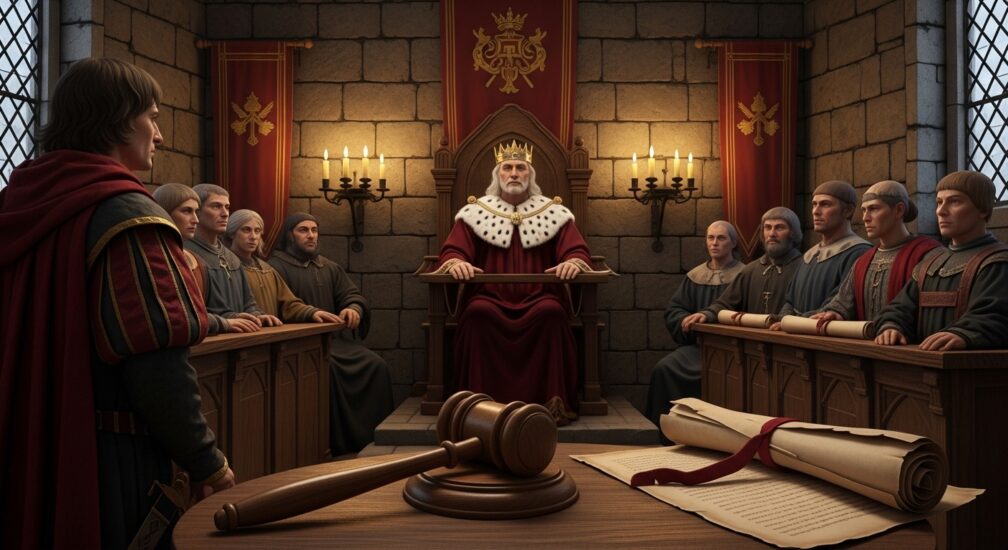
Medieval English common law, one of the most influential legal systems in history, has profoundly shaped modern British and American legal frameworks. This system, born from the monarchy’s need to standardize rules across England, is more than just a historical artifact-it’s a legacy that continues to affect contemporary law. Understanding its core principles and how it laid the foundation for modern jurisprudence can provide essential insights into the structure of today’s legal systems.
The Origins of Medieval English Common Law
Medieval English common law originated in the 12th century under King Henry II, who sought to unify the diverse legal customs across England. Unlike the Roman law, which was codified, common law was based on judicial precedents-decisions made by judges in past cases. These decisions, based on customs and statutes, created a framework that applied equally to all subjects, breaking away from feudalism’s localized rules. The creation of a single legal system was a monumental shift from the fragmented legal systems of earlier times, where each region or family upheld its laws.
The role of the monarchy in consolidating law cannot be overstated. King Henry II’s reforms also included the establishment of royal courts, which, for the first time, allowed commoners to bring cases before the king’s justices. This was a major departure from earlier practices, where the nobility and clergy had their own courts. It helped set the groundwork for the feudal system that intertwined land ownership with legal responsibilities.
Key Features of Medieval English Common Law
At its core, medieval English common law was built on several key principles that still influence the legal systems of Britain and the United States today:
- The Concept of Precedent: This is perhaps the most important feature of common law. Judges relied on past judgments to inform their decisions. Over time, this created a body of case law that became a reference point for future legal cases, a system still in place in today’s legal practices. This concept is the jurisprudence that has influenced numerous statutes and writs in modern courts.
- The Role of Trials and Petitions: Trials in medieval England were an essential part of the legal system. Common law introduced the notion of trials by jury, allowing citizens to have a say in the legal process. It also enabled individuals to petition for justice, a custom that still exists today. The principles of litigants being able to challenge and uphold laws remain central in courts today.
- The Concept of Royalism and the Monarch’s Role: The legal system under the monarchy was not only focused on enforcing laws but also maintaining the king’s authority. Monarchs often had the final say in legal matters, ensuring that laws were uniformly applied across the kingdom. This system influenced the future structure of legal authority and helped stabilize the kingdom.
- Inheritance and Land Ownership: Vassals and landowners had legal responsibilities toward each other. Landownership was not only a form of wealth but also a form of legal responsibility. The common law system codified inheritance rules, ensuring that property rights and legacies were preserved.
- Charters and Writs: Medieval legal documents such as charters and writs became tools through which legal claims and judgments were formalized. Writs, in particular, were used to command action by a royal court. These documents were the precursors to modern legal instruments such as contracts and deeds.
How Medieval English Common Law Influences Today’s Law
The legacy of medieval English common law continues to shape modern legal systems, particularly in British and American law. One of the main features of medieval common law still in use today is the doctrine of precedent. It serves as the cornerstone of case law and is fundamental in courts across the globe. The British system of common law still uses the writ system in some form, and the American legal system heavily relies on precedents set in earlier cases.
In particular, the medieval English system in which groups of families agreed to uphold the law laid the foundation for community-based legal practices that we see in modern law. Though much of the personal control over the law was eventually overtaken by the central government, the importance of common law in shaping civil rights, property laws, and criminal justice is immeasurable.
The US Gun Control Debate and Medieval Law
Interestingly, one of the debates in modern American society-how a medieval English law affects the US gun control debate-has its roots in common law. The Second Amendment, which grants the right to bear arms, traces back to the English Bill of Rights of 1689, which was influenced by English common law’s recognition of the right to self-defense. This principle, which originates in medieval times, shows how deeply entrenched medieval law is in shaping modern democratic societies.
Medieval English common law is a complex but enduring system that laid the groundwork for modern legal systems. The historical significance of medieval English law, its system of justice, and its impact on modern jurisprudence cannot be overstated. By understanding the fundamental principles of medieval common law, such as its reliance on precedent, the importance of land and property rights, and its widespread influence on legal systems today, we can better appreciate the law’s evolution and the importance of maintaining such a system.For more on the history of medieval law and its impact, visit the Medieval Torture Museum in Chicago, Medieval Torture Museum in LA, and Medieval Torture Museum in St Augustine. Also visit our blog. We dive deeper into these captivating historical details for you!